Nursing Care Plan for Pneumonia
8 Pneumonia Nursing Care Plans
August 3, 2015 – 02:59 pm
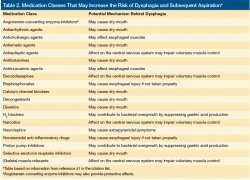 Preventing Aspiration Pneumonia by Addressing Three Key Risk
Preventing Aspiration Pneumonia by Addressing Three Key Risk
| Assess the rate and depth of respirations and chest movement. | Tachypnea, shallow respirations, and asymmetric chest movement are frequently present because of discomfort of moving chest wall and/or fluid in lung. |
| Auscultate lung fields, noting areas of decreased or absent airflow and adventitious breath sounds: crackles, wheezes. | Decreased airflow occurs in areas with consolidated fluid. Bronchial breath sounds can also occur in these consolidated areas. Crackles, rhonchi, and wheezes are heard on inspiration and/or expiration in response to fluid accumulation, thick secretions, and airway spams and obstruction. |
| Elevate head of bed, change position frequently. | Doing so would lower the diaphragm and promote chest expansion, aeration of lung segments, mobilization and expectoration of secretions. |
| Teach and assist patient with proper deep-breathing exercises. Demonstrate proper splinting of chest and effective coughing while in upright position. Encourage him to do so often. | Deep breathing exercises facilitates maximum expansion of the lungs and smaller airways. Coughing is a reflex and a natural self-cleaning mechanism that assists the cilia to maintain patent airways. Splinting reduces chest discomfort and an upright position favors deeper and more forceful cough effort. |
| Suction as indicated: frequent coughing, adventitious breath sounds, desaturation related to airway secretions. | Stimulates cough or mechanically clears airway in patient who is unable to do so because of ineffective cough or decreased level of consciousness. |
| Force fluids to at least 3000 mL/day (unless contraindicated, as in heart failure). Offer warm, rather than cold, fluids. | Fluids, especially warm liquids, aid in mobilization and expectoration of secretions. |
| Assist and monitor effects of nebulizer treatment and other respiratory physiotherapy: incentive spirometer, IPPB, percussion, postural drainage. Perform treatments between meals and limit fluids... |
Source: nurseslabs.com
Interesting facts
 Tuberculosis, MTB, or TB (short for tubercle bacillus) is a common, and in many cases lethal, infectious disease caused by various strains of mycobacteria, usually Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Tuberculosis typically attacks the lungs but can also affect other parts of the body. It is spread through the air when people who have an active TB...
Tuberculosis, MTB, or TB (short for tubercle bacillus) is a common, and in many cases lethal, infectious disease caused by various strains of mycobacteria, usually Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Tuberculosis typically attacks the lungs but can also affect other parts of the body. It is spread through the air when people who have an active TB...
You might also like

Nursing Care Plan for Appendectomy

Care Plans
Popular Q&A
Related Posts